
An In-Depth Look at Formulation Compliance, Ingredient Safety, and Functional Performance
As the global demand for wet wipes continues to expand — driven by hygiene awareness, baby care, household cleaning, and personal disinfection — so does the regulatory scrutiny around formulation safety, functionality, and product claims. In China, a key manufacturing and export hub for wet wipes, a new set of national standards will reshape how wipes liquid — the core component of any wet wipe — must be developed and evaluated.
The updated regulatory framework includes the mandatory GB 15979-2024 Hygienic Requirements for Disposable Hygiene Products, along with a comprehensive GB/T 27728-2024 standard series covering general, baby-specific, and disinfectant wipes. Together, they form the most stringent regulatory landscape China has seen for this category.
Understanding the implications of these standards — particularly on wipes liquid formulation — is essential for manufacturers, OEM/ODM factories, and global brand owners who either produce in China or source products from Chinese suppliers.

1. Why the Liquid Component Matters More Than Ever
While the substrate (non-woven fabric) and packaging contribute to a wipe’s form and usability, the wipes liquid defines its function. Whether a wipe is designed for gentle baby care, aggressive surface cleaning, or antimicrobial performance, it is the liquid phase that delivers those benefits — and that attracts the most regulatory attention.
The 2025 GB standards require full disclosure and compliance not only in terms of what is in the liquid, but also how it behaves: its pH, antimicrobial effectiveness, preservative system, and potential risks (e.g., skin irritation, sensitization). Therefore, any formulation updates to comply with these standards must begin with a re-evaluation of the wipes liquid from the ground up.
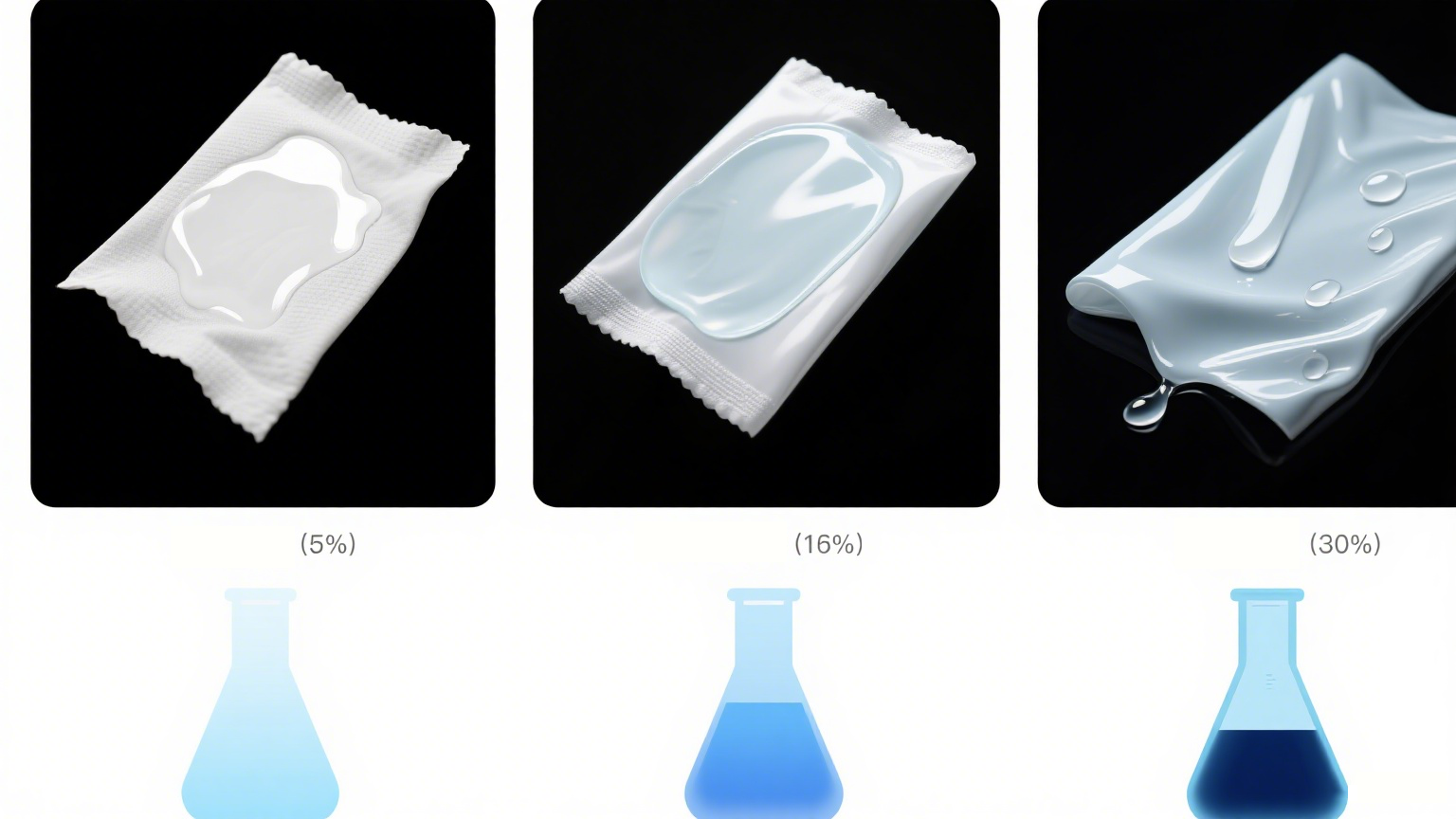

2. Key Changes in the 2025 Chinese GB Standards Affecting Wipes Liquid
2.1 Ingredient Restrictions
The new GB 15979-2024 bans or restricts several categories of ingredients in wipes liquid, including:
MIT/CIT (Methylisothiazolinone / Chloromethylisothiazolinone) – common but increasingly restricted preservatives
Hormones, antibiotics, and pharmaceutical actives
Optical brighteners, fluorescent agents, and recycled raw materials
Heavy metals (e.g., lead, cadmium, arsenic) beyond strict thresholds
Fragrances or alcohol in baby wipes
This shift mirrors international trends, especially in the EU and North America, and reflects China’s increasing alignment with global consumer safety expectations.
2.2 Functional Claims Must Be Evidence-Based
If a wipes product claims to be “antibacterial,” “disinfecting,” or “kills 99.9% of germs,” its wipes liquid must include verifiable active ingredients — such as ethanol, quaternary ammonium compounds, or natural antimicrobials — at proven effective concentrations.
Under GB/T 27728.3-2024 (Disinfecting Wipes), manufacturers must:
Specify active ingredients and their exact percentages
Conduct microbiological testing against target organisms
Maintain supporting data for regulatory review or audit
2.3 Baby Wipes Are Categorized Separately
A separate standard (GB/T 27728.2-2024) outlines specific requirements for baby wipes, focusing heavily on the safety of the wipes liquid:
No alcohol, essential oils, or potentially sensitizing preservatives
pH must be adjusted close to skin neutrality (5.0–6.5)
Skin irritation and sensitization testing is strongly recommended
Ingredients must align with cosmetics-grade safety profiles
The liquid formula must be exceptionally gentle, often requiring custom preservative systems and the elimination of fragrance or dye components.
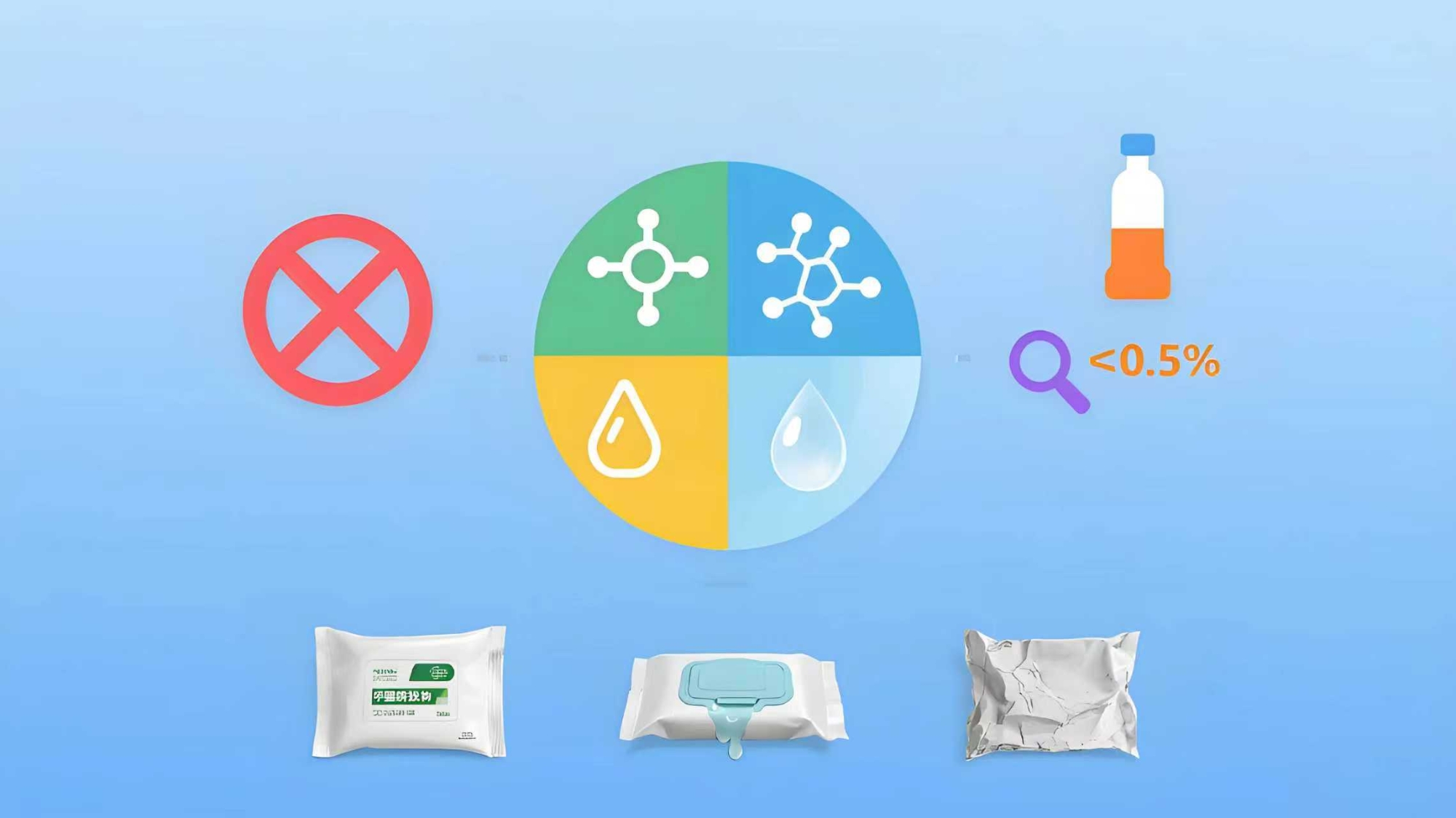

3. Formulation Considerations for Compliant Wipes Liquid
Designing a wipes liquid that complies with these new regulations — while also performing well in the field — requires thoughtful formulation across multiple dimensions.
3.1 Raw Material Quality
All ingredients used in the wipes liquid should be:
Traceable and supported by technical documentation (MSDS, COA)
Sourced from suppliers with quality certifications (e.g., ISO, GMP)
Free from restricted or high-risk substances (e.g., formaldehyde donors, parabens, colorants)
3.2 Preservation Strategy
Preservatives must balance microbial control with user safety. Under the new GB standards, harsher preservatives like CIT/MIT are banned in many wipe categories. Safer alternatives may include:
Food-grade preservatives (e.g., potassium sorbate, sodium benzoate)
Natural antimicrobial agents (e.g., organic acids, plant extracts)
Encapsulation or combination systems to enhance efficacy at low dosages
Stability testing over time and across temperatures is essential to ensure the wipes liquid resists contamination during storage and use.
3.3 Functional Additives
Depending on the wipe’s intended use, the liquid may include:
Moisturizers (e.g., glycerin, panthenol, aloe vera)
Surfactants (e.g., mild ethoxylates or glucosides for cleaning wipes)
Antimicrobial agents (e.g., ethanol, benzalkonium chloride)
pH adjusters to maintain skin-friendly levels
Fragrances — only when permitted by category and used within safe thresholds
3.4 Physical Properties of the Liquid
The texture, spreadability, evaporation rate, and interaction with the non-woven fabric are all influenced by the liquid’s physical parameters. These include:
Viscosity
pH stability over time
Color and clarity
Foam characteristics
Non-stickiness after application
These aspects impact both user experience and product shelf-life.
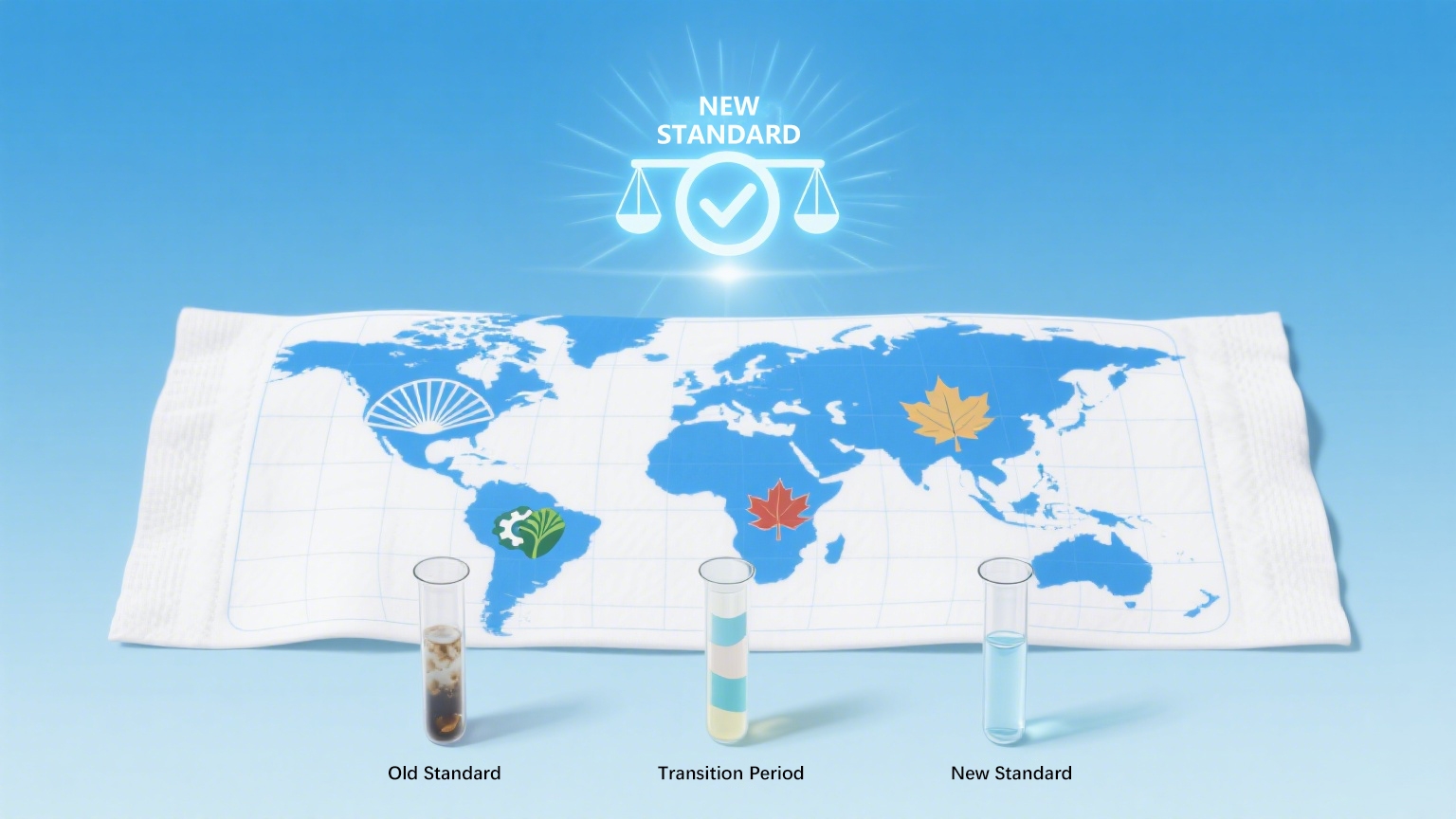
4. Global Relevance of China’s New Standards
While GB standards are national regulations, their relevance extends beyond China for several reasons:
OEM/ODM factories in China supply brands worldwide — many global wet wipes are manufactured in facilities that must now comply with GB standards.
Chinese exports to Southeast Asia, Africa, South America, and the Middle East often serve as category leaders in emerging markets.
Global brand owners increasingly demand multi-region compliance, including with Chinese GB, EU REACH, and US FDA OTC standards.
In this sense, compliance with the 2025 Chinese standards makes a wipes liquid formulation more globally credible — not just nationally acceptable.

5. Outlook for Manufacturers and Brands
The transition to GB 15979-2024 and GB/T 27728-2024 represents an opportunity, not just a challenge. It allows manufacturers to:
Modernize their wipes liquid formulations with safer, more sustainable components
Strengthen product performance and claim substantiation
Improve alignment with international expectations in consumer health and regulatory transparency
Differentiate products through better skin compatibility, verified disinfection, or natural profiles
For contract manufacturers and private label brands, adopting fully compliant wipes liquid formulations ensures smoother regulatory reviews, more robust product claims, and a stronger foundation for export and long-term market trust.
Final Thoughts
In a product category where the liquid is everything, understanding how to formulate safe, functional, and compliant wipes liquid is now a core competency — not a nice-to-have.
The 2025 Chinese GB standards will drive significant quality improvements in wet wipes, and companies that prepare early — by reassessing their liquid bases — will be best positioned to succeed in both the domestic and global markets.





 English
English
 USA
USA
 西班牙语
西班牙语
 俄罗斯
俄罗斯
 葡萄牙
葡萄牙
 印尼
印尼
 巴基斯坦
巴基斯坦
 尼日利亚
尼日利亚
 孟加拉
孟加拉
 墨西哥
墨西哥
 越南
越南
 日本
日本
 韩国
韩国

